Striving to maintain a healthy and balanced lifestyle with a diet full of nutrient-dense foods is ideal, but sometimes this can be challenging. For the past few months, especially, we have all been swept into the new reality of working-from-home, home-schooling and coping with the stress caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, which may have affected our regular healthcare regiment to a large extent.
However, treating your body well is not only crucial for our physical but also our mental health. So for those of you who have been lacking their vitamins lately, here are six essential nutrients, their functions and recommended Japanese foods that contain them, that we should always try to fit into our diets — especially when we’re extra busy or stressed.
1. Vitamin C for Healthy Skin
Vitamin C has healing and antioxidant powers helping to block some of the damage caused by not only free radicals (exist in pollutants in the air) but also the sun. Vitamin C also plays an essential role in facilitating the growth, development, and repair of bodily tissues, bones and teeth. Often used as an ingredient in skincare products, Vitamin C can help your body produce collagen — an essential protein used to make skin, cartilage, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels.
Signs that may indicate you’re running low: Bleeding gums, dry, scaly skin, sensitivity and proneness to bruising, and sometimes nose bleeds
How much do you need? The Recommended Daily/Dietary Allowance (RDA) for vitamin C is around 75mg for women and 90mg for men. Pregnant women should increase their intake to 85mg and during breastfeeding to 120mg. Smokers require 35mg/day more than non-smokers. Some wound and alternative care treatment plans can be as much as 2000mg or more.
Where to find it: Acerola Cherries, Kiwi, Kaki (Japanese Persimmons), Citrus fruit
You can easily find all of the above in Japan – whether infused in a drink, found in a skincare product, or even as part of a beautiful dessert. For the Japanese, acerola has been celebrated as a summer fruit that tastes wonderful, is healthy and packed with vitamin C. Just half a cup of acerola cherries gives you a massive boost of Vitamin C – more than 900% of the daily minimum.
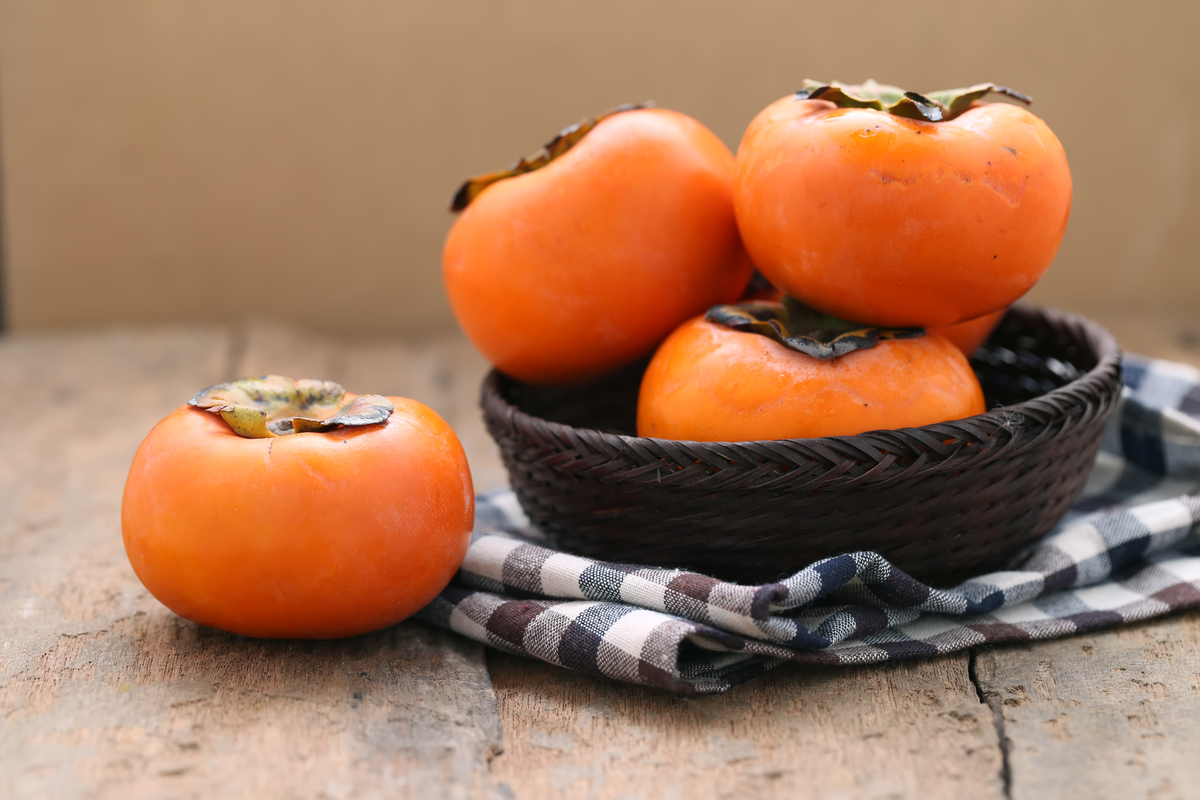

Kaki, or Japanese persimmons (pictured above), are also packed with nutritional goodness. Known for their honey-like flavor, kaki are loaded with important vitamins and minerals, including A, C, a variety of Bs, potassium and manganese. Kaki are also low calorie but high in fiber, making them a diet-friendly fruit with added beneficial plant compounds like tannins and flavonoid antioxidants.
2. B12 for Energy
Vitamin B12 is one of the eight B-vitamins that are essential for the normal function of our nerve cells and is also a key vitamin in the formation of red blood cells. What makes vitamin B12 particularly important is that it functions to maximize our metabolic efficiency, in other words, how we use our energy. It is also important in helping us maintain a healthy body weight, keeping our eyes, skin, hair and nails looking good and helps regulate our hormones, which, as a combined result, moderates our mood.
Signs that may indicate you’re running low: You’ve tried different suggestions to overcome constantly feeling tired and sluggish, but for some reason, nothing is working and you have no idea why. You’ve made a considerable effort to get more sleep, you’ve been more mindful of your stress and work-life balance, and even started with a new yoga meditation routine. But, you’re still tired. If you’re feeling sluggish, a little down, or have a sudden outburst of acne on your chin or around your mouth, chances are you’re short on vitamin-Bs. Other signs that you need a vitamin B boost include feeling faint, sluggish metabolism leading to weight gain, loss of muscle tone, feeling distracted and even irritated.
How much do you need? The RDA for vitamin B12 for both women and men is 2.4 mcg and will slightly increase between 2.6mcg to 2.8mcg for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Where to find it: Eggs and Saba (Japanese mackerel)
The average Japanese person eats around 320 eggs per year. Whether in an omelet form, on top of sushi, raw over rice, or mixed with chicken or other meats, tamago is enjoyed in both sweet and savory form, holding its value as not only a delicious ingredient but also a healthy one. A single boiled egg has approximately 80 calories, about 8g protein, 5g healthy fats and is loaded with vitamins A, E, D, K, almost the full range of Bs, selenium, phosphorus and zinc. One egg (including yolk) contains approximately 0.6mcg of B12 and so consuming 2 to 3 large eggs per day (which is safe for healthy people) gives you about half of your daily recommended value.
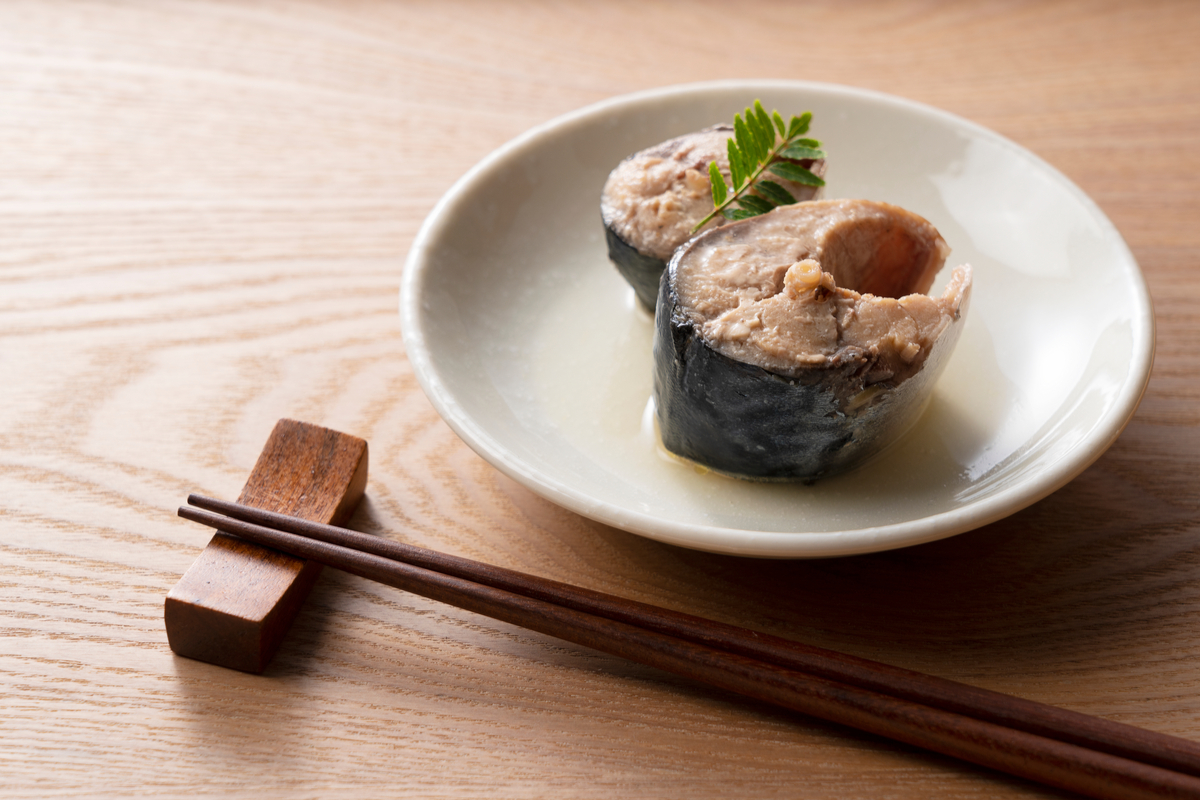

Saba is one of the healthiest fish you can eat. In Japan, it’s enjoyed in many ways, from sashimi to grilled, boiled and even canned. It’s high in proteins, vitamins, minerals and a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids but also provides about six times the daily recommended intake of vitamin B12 — approximately 12mcg for every 100 grams. Found all year round and in just about every Japanese teishoku or izakaya restaurant, this healthy (and yummy) fish helps support healthy and strong muscles, is good for your skincare hair and contributes to a more robust immune system.
3. Calcium for Proper Posture
Calcium is essential for optimal bone health, strong teeth and proper muscle function. Women start losing bone density already their 20s and to prevent the onset of osteoporosis, it’s important to start getting plenty of it now. Bone loss in women is associated with hormonal changes. Estrogen is the female hormone that helps to protect the bones and so when a woman is either pregnant or entering the first stages of menopause, it’s especially important to consider taking a calcium supplement. Most healthy men don’t need to take calcium supplements — obtaining one’s daily dosage can be done through healthy eating habits. That being said, calcium is just as crucial for men as it is for women, as it is an essential nutrient for not only optimal bone health but also for your nervous system as it helps muscles and nerves carry necessary signaling between the brain and every part of the body.
Signs that may indicate you’re running low: Calcium deficiency can worsen from feeling tired to extreme exhaustion, have insomnia, brittle nail and poor skin condition, but also increase PMS symptoms. In more severe cases, it can lead to osteoporosis, osteopenia, and even depression.
How much do you need? The RDA is between 1,000 and 1,200 mg per day for adults depending on age.
Where to find it: Tofu
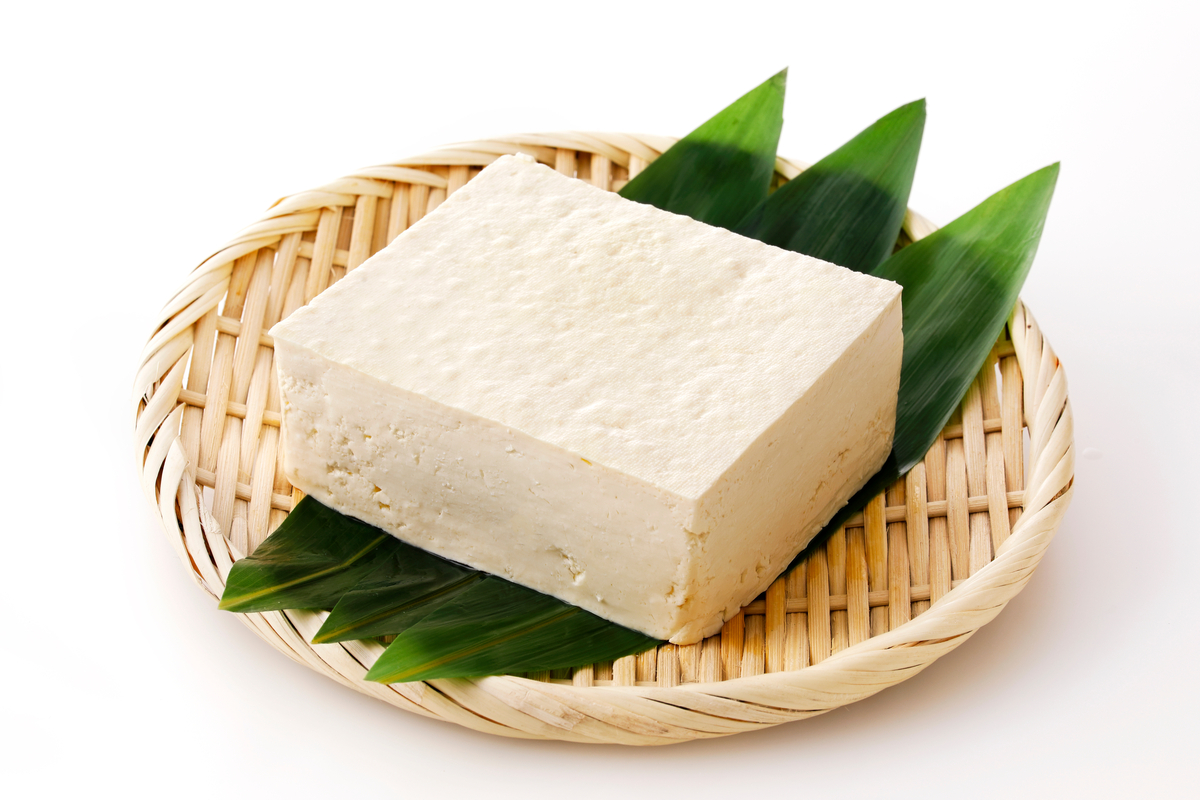

Tofu is low in fat, high in protein, and is made from soybeans, which are relatively easy and sustainable crops to harvest. It’s loaded with essential nutrients — mainly calcium and magnesium, which are particularly beneficial to women’s health and hormonal regulation. Served cold in the summer months and boiled in broths during the winter, tofu can be enjoyed in a variety of ways. Traditionally made tofu contains about 180mg of calcium per 100 grams. For those of you who are vegan or vegetarian, tofu is still one of the wealthiest plant-sources of protein so this Japanese ingredient is something you should be adding to your routine more than five days a week.
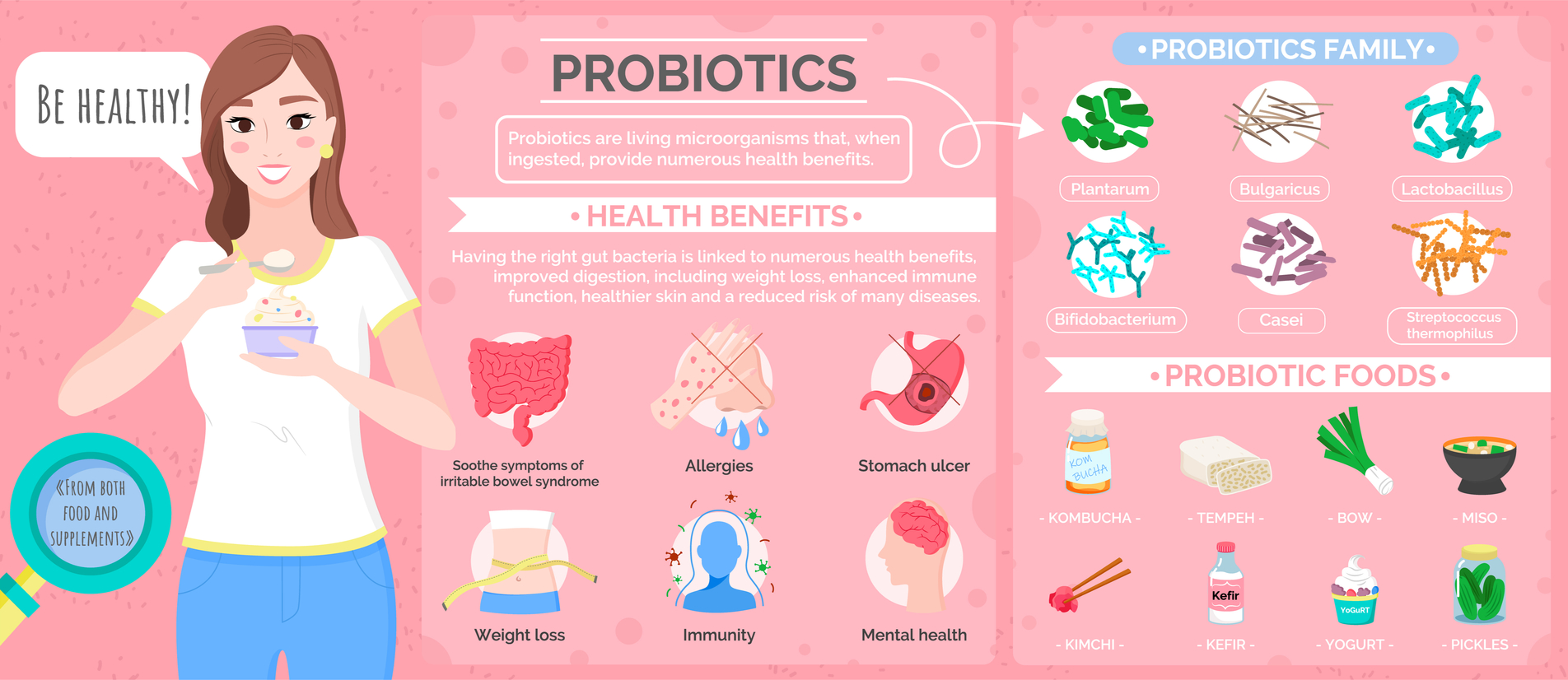
4. Probiotics for a healthy belly
There are plenty of ads and posts about maintaining a healthy microbiome in your body: Healthy bacteria in your belly to promote a healthier you. And they’re right! More and more research indicates how important our belly health is to maintain a balanced, disease-free, and optimal state of well-being. Probiotics are live microorganisms that can be consumed either through fermented foods or supplements. They promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria and have positive benefits for weight regulation, digestive health, immune function and can even help treat many illnesses, including yeast infections, UTIs, and IBS.
Signs that may indicate you’re running low: The most common symptoms that your belly is not at its best includes a constant upset stomach, unintentional weight gain or loss, constant fatigue and/or difficulty sleeping, skin irritations and sudden food intolerances.
How much do you need? Healthy adults can consume anywhere up to 1-10 billion CFUs of probiotics from food or supplements daily — the amount contained in a supplement capsule or two.
Where to find it: Miso and natto (Japanese fermented soybeans)
Miso is another staple of Japanese cuisine. From miso soup to miso-marinated fish, to sauces for meats, veggies, and hey, it’s even in ramen! Miso is pretty much everywhere in Japan and there’s no wondering why. It’s made from fermented soybeans, which are processed into a thick paste that can be used easily for cooking. Miso contains millions of beneficial bacteria, which makes it one of Japan’s superfoods. Some studies reported that frequent miso soup consumption was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer in middle-aged Japanese women. Another study found that women who consumed a regular amount of miso had a reduced risk of stroke. Definitely worth adding to our diets.
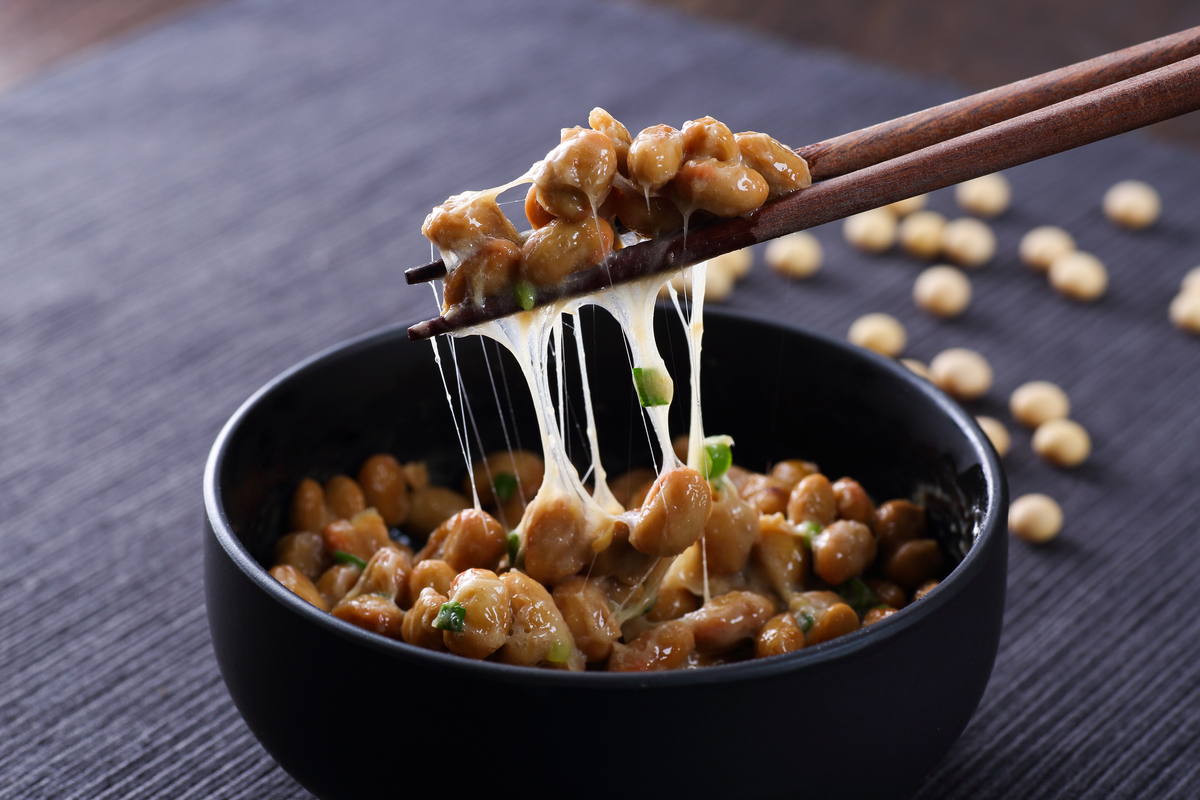

Sticky, gooey and stinky, natto is often eaten with white rice in the morning, in maki sushi rolls or sometimes added as an extra topping to your soba or udon noodles. With its superfood status, natto is becoming more and more popular in healthy diet regimes and as a result, natto inspired meals are also finding their way into cookbooks, magazines, and of course, social media. Natto is not the most appealing of Japanese foods, but it’s one that is incredibly nutritious. It’s one of the cheapest gut-friendly agents you can find in Japanese supermarkets that contains fiber, probiotics, vitamin K2 and nattokinase (aslo believed to all contribute to reducing high cholesterol and blood pressure) all at once.
Women-exclusive vitamins and minerals
5. Iron for PMS Rescue
It’s that time of the month again and the lineup of aches, pains, mood swings, and even distractions begin to hit us. Iron is not only an essential micronutrient that should be consumed daily but should be consumed even more so when women are on their periods because, you know, we’re losing a lot of it. Iron is an essential component of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout our bodies via red blood cells. It’s also important for the production of red blood cells, which helps to support our immune system and our cognitive processes, temperature regulation, and healthy cell growth and rejuvenation. Since many of us are leaning towards plant-based diets or at least cutting back on red meats, it’s advised to take an iron supplement or a women’s supplement, which will often have the RDI for iron covered.
Signs that may indicate you’re running low: Feeling tired, short of breath, distracted, light-headed, agitated, weak, and/or generally unwell
How much do you need? The RDA of iron for women ranges from 15-18mg/day for women who are menstruating and around 8mg/day for menopausal and postmenopausal women
Where to find it: Shellfish

Living in Japan means we have access to some of the best seafood in the world. Clams, mussels, oysters, and even squid and octopus are full of nutrients like zinc — which is important for him if you’re trying to conceive — and are a high source of iron, which is good to know if you’re a pescatarian or flex-vegetarian. Next time you’re PMSing, why not try to swap those fried or starchy food-cravings for some iron-rich clams or even grilled tako — you’ll feel surprisingly better!
6. Folic Acid (Vitamin B9) for a Healthy Pregnancy
Folic acid is an especially important micronutrient because it helps to generate new and healthy cells. If you’re planning on getting pregnant or already are, it is greatly advised to take prenatal vitamins because they contain elevated amounts of iron, folic acid (folate), omega-3s and many more. Folate is particularly important during pregnancy because it helps prevent NTDs (neural tube defects), such as spina bifida and anencephaly. Make sure you consult your obstetrician or gynecologist for further information and guidance during your pregnancy.
Signs that may indicate you’re running low: Symptoms such as feeling extreme amounts of fatigue, bruising easily, dizziness, or even feeling short of breath
How much do you need? The RDA of folic acid for all women is 300-400 mcg daily. Women who are planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant should get 500-600 mcg of folic acid from a supplement and a natural diet.
Where to find it: Komatsuna (Japanese spinach)
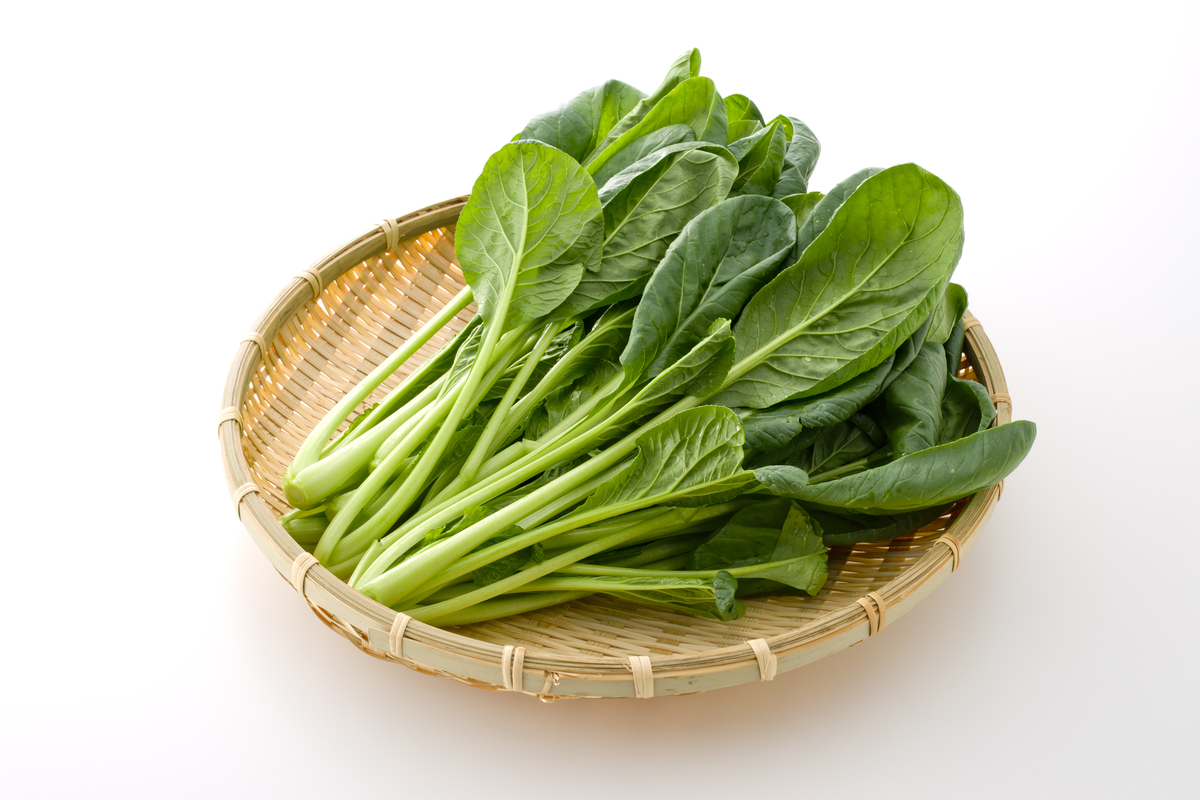

Komatsuna, also known as Japanese spinach, has been around since the Edo period and is named after the area it was originally grown: the Komatsugawa region. This is a common green found in most Japanese households as it can be consumed in a variety of ways — from raw to steamed, sautéed, boiled, and even fried. It is available all-year-round at most grocery stores and for a price that you won’t bat an eyelash for.
A healthy, beautiful and balanced you is achieved when you pay as much attention to your nutrition as you do to your skincare or fashion picks. Vitamin deficiencies can manifest in different ways, often starting with our skin. Eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, healthy proteins and fats — and we mustn’t forget about those friendly bacteria for our bellies — will help make you function at your optimal self!
Emi Schemmer has a degree in Health Sciences and post-graduate certification in Nutrition and Holistic Medicine. She is currently developing her own skincare line inspired by natural products.